The knee is more susceptible to injuries and various diseases than other joints.A significant number of orthopedic traumatologist and rheumatologist patients complain of severe knee pain.This article will tell you what to do if you suddenly experience severe pain.You are being treated, the point is to seek medical help with your problems in time.
What exactly hurts your knee?
The knee joint is the most complex joint, as it bears the main load.Its structure: three bones (the femur, tibia and patella form a single trochlear joint, which consists of two interconnected joints: femorotibialis (tibiofemoralis) and femoralis-patellofemoralis (patellofemoralis).
The patella is a flat sesamoid (accessory in the joint) bone that attaches to the head of the femur, slides in a concave groove, and acts as a block.Structural characteristics: the anterior surface of the patella is covered by periosteum, and the posterior surface connecting to the femur is covered by hyaline cartilage.The patella is strengthened by ligaments: main and lateral - vertical (upper and lower) and horizontal (lateral - inner and outer).
O transmits the force of the quadriceps femoris muscle to the locomotor formations of the leg, ensuring knee joint extension of the leg.The surface of the articular bones is covered with cartilage, which acts as a shock absorber.Additional shock absorbers that protect the joint from injury are two crescent-shaped cartilaginous menisci located between the femur and tibia.The joint is held in the correct position by ligaments, tendons and the surrounding capsule.
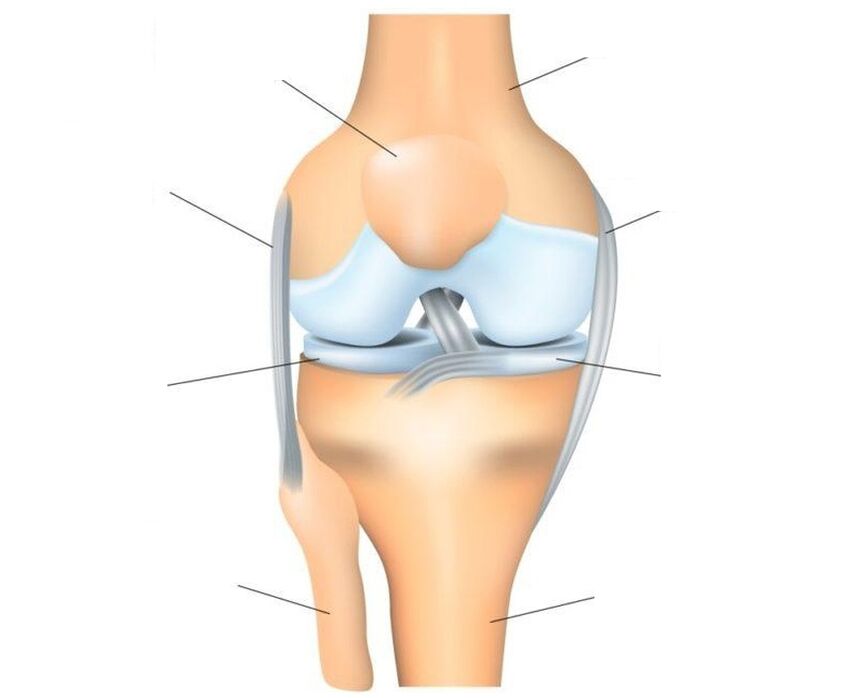
Injuries and diseases affect different joint tissues.Not everyone can get sick.Thus, the cartilage tissue has no nerve endings, so it can die unnoticed and painlessly.But the ligaments and joint membrane have many nerve endings, and in case of injury or inflammatory processes, they immediately begin to react, which manifests itself in the form of severe pain.In case of significant destruction of the articular cartilage, the pain may involve the periosteum, the well-innervated outer layer of bone, in the process.
What to do if you have severe knee pain
Intense knee pain can appear suddenly or develop gradually.In any case, it often becomes unbearable.If severe pain occurs, you should calm down and seek medical help immediately.All of this can be treated, and the specialists will be able to help even in the case of an advanced disease.If you can't see a doctor right now, you can temporarily relieve the pain on your own.
But you must remember that if you have pain in the knee joint, this is a temporary measure;you should still seek medical help;can't be without it.And we better not be late.
How to treat knee and leg pain at home
You can take the following emergency measures to alleviate the condition of severe pain in the knee joint:
- Treat the pain with pills.
- Use external pain relievers (ointments, gels).
- Injections.If tablets and external agents do not have an effect, the drug is administered as an intramuscular or subcutaneous injection.
Many medicines are available without a prescription at the pharmacy.
In the case of chronic knee joint pain, when there is no significant inflammation, you can perform physical exercises that strengthen the musculo-ligamentous system, improve blood circulation and metabolism.Systematic training leads to a gradual decrease in pain, despite the fact that the legs are quite crunchy.
Approximate exercise sequence for knee pain:
- Fixed knee.Lie on your back, bend one leg at the knee, lift it up and hold it in this position for a minute;the second leg is motionless in this case;straighten and lower your leg very slowly, rest for 10 seconds and repeat the exercise with the other leg;repeat 10 times;
- Double leg bend with knees close to face.Lie on your back, bend your legs at the hips and knees, fix the latter near your face and hold it for a minute.Then slowly straighten and lower your leg, rest for 10 seconds and repeat;perform 5-6 approaches, gradually increasing the load.
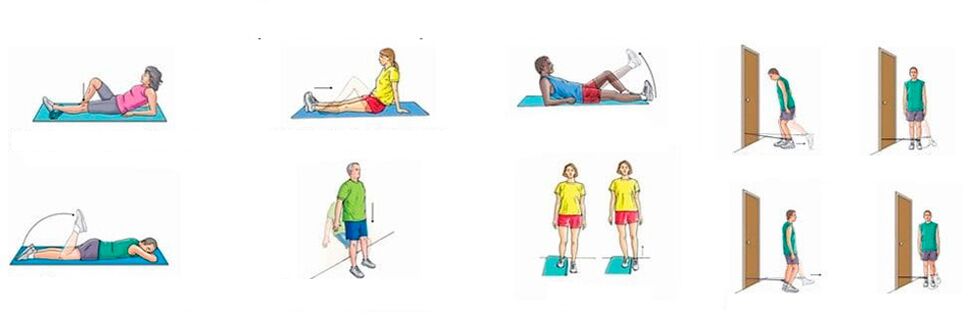
Acute knee pain requires rest;all physical activity and training are contraindicated.
If there is acute pain in the knee joint, accompanied by swelling and redness of the skin, violation of the general condition, fever, the leg cannot be moved, it must be kept at rest.And only after the inflammation begins to subside, you can first switch to passive exercises (performed by an assistant), and then to active exercises (performed by the patient himself).
What not to do if you are in pain
For chronic pain, the following are not allowed:
- bruised knee - you can avoid this if you organize your life in such a way as to minimize the risk of injury;
- excessive body weight is an additional burden on the knees, especially in the elderly;
- heavy physical activity, jumping, strength sports;You should also not run;
- any poisoning, so you need to get rid of bad habits (smoking, alcoholism), treat all chronic diseases and foci of infection;
- wearing uncomfortable tight shoes, high heels;
- stress, lack of sleep;
- sedentary lifestyle - you need to force yourself to move at certain intervals.
Warm compresses cannot be used even without a doctor's prescription: in the case of purulent and hemorrhagic processes (with intra-articular bleeding), they can cause irreparable damage.
When you need to see a doctor urgently
If your knee hurts, you need urgent medical attention if the following symptoms appear:
- swelling, redness and tenderness in the knee combined with fever and general malaise;
- severe knee pain immediately after the injury or for some time afterwards;
- gradual increase in pain intensity;
- periodic pain after physical exertion, prolonged standing, sharp straightening of the leg;
- night pain and associated insomnia;
- if the pain in the knee is very strong and constant, the feeling is that the inside of the kneecap hurts.
In any case, knee pain should be a reason to see a doctor.There is no point in treating yourself: it can temporarily reduce or even eliminate pain, but it does not stop the progression of the disease and the destruction of the joint.The treatment must be entrusted to a specialist.
What to do for different types of severe knee pain
Painful sensations in the knee can vary in nature and duration between people.They can hurt constantly or develop only under certain loads, at night, etc.For example, some pathological processes are characterized by knee pain when bending, others - knee pain when walking, etc.Only a specialist can figure out exactly what and why it hurts, and how to help the patient.
Knee pain caused by coronavirus and other viral diseases
Viral infections can cause arthritis.Usually, these diseases develop against the background of an existing infection and pass without consequences after its termination.Thus, in the case of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections accompanied by acute fever, both short-term joint and muscle pains and acute arthritis with inflammation and swelling of the knee joints may occur.Their course is favorable.
The coronavirus infection has its own characteristics: it occurs differently in each patient.Why this happens is not known.During the course of the disease, sometimes aching joint pain, swelling and redness appear - a sign of acute arthritis, but then they disappear.
Arthritis, which begins about a month after contracting the coronavirus, is more dangerous.The fact that it has a significant effect on the immune system.Dysfunctions of the immune system lead to the development of autoimmune processes.This is especially dangerous for those whose close relatives suffer from chronic arthritis.Experts note that such patients are at high risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis (RA).The first sign of RA is morning stiffness (difficulty bending the knee).
If you develop arthritis after recovering from a viral infection, see a rheumatologist immediately.
Severe pain under the knee
This may be a sign of a Baker's cyst - an enlarged synovial bursa with fluid in the popliteal area.The cyst and the associated pain below the knee are due to the fact that it is connected to the cavity of the knee joint and is filled with synovial fluid.In this case, the reverse flow of the liquid is difficult for various reasons.Most often, the cyst develops against the background of bruises, arthrosis and knee arthritis.
A small cyst can go unnoticed for years.However, its considerable size compresses the surrounding tissues, causing pain below the knee that increases with physical activity, including walking and running.Women are sick more often.Sometimes the cyst disappears on its own, but often it progresses and increases in volume, which can lead to rupture or suppuration.
If you feel pain below the knee, it is better to see a doctor as soon as possible.Conservative (removal of fluid from the cyst, injection of glucocorticoids) and surgical (removal of the cyst) treatment is performed.
Severe pain in the left or right knee
Severe pain combined with swelling and redness of the skin above the right or left knee usually indicates the development of an acute inflammatory process.It can be acute non-specific arthritis (the process can become purulent), reactive arthritis, which begins a few days after a urogenital or intestinal infection.Both diseases present with similar symptoms;a correct diagnosis can only be made after a complete examination.
The right or left knee can suffer microtraumas, for example, in athletes or workers in certain professions who use one (usually the right) knee more than once.
It is important not to use folk remedies at an early stage, but to carry out the appropriate treatment, this will allow you to fully recover and forget about the pain forever.But even in the case of advanced diseases, the specialist can always provide help and alleviate the pain.
Knee and leg pain
Depending on the cause, course of the disease and the presence of complications, severe knee pain may include:
- in the tibia below the knee– rare, this may indicate compression of the nerve branches innervating the muscles of the leg by the inflamed, swollen periarticular tissues in the knee area;pain below the knee in the back indicates compression of the branches of the sciatic nerve, and pain below the knee in the front indicates involvement of the nerves innervating the front surface of the leg;Such diseases are treated by a rheumatologist, but consultation with a neurologist is necessary;
- above the knee, into the thigh– often a sign of a post-traumatic inflammatory process in the femur-patella joint;in this case, patellofemoral pain syndrome develops;the pain is strong, aching, sometimes jerking, which is aggravated by walking;an orthopedic traumatologist and a rheumatologist help to cope with pain;
- from the side, from the inside– pain may develop with injury and damage to the inner lateral articular ligament;strong, jerking pain in the side, with hemarthrosis (intra-articular bleeding) - exploding, accompanied by joint imbalance, the whole leg crunches during movement;the same pain occurs when the external ligament is sprained;the help will be provided by an orthopedic trauma specialist.
In order to eliminate the pain, you need to determine the exact cause of it, and this is impossible to do on your own.You need medical help.
Patella pain in back, front and side
Patellar pain is almost always the result of acute or chronic injuries:
- so knee pain- the causes are related to damage to the femoral-patella joint with the development of patellofemoral pain syndrome;the pain is aching, constant, worsens when walking;
- from– such painful sensations are caused by superficial bruises of the knee or frequent, prolonged standing of the knee with microtrauma of the patella;the pain is significant, as the periosteum, rich in nerve endings, is damaged;
- lateral knee painin case of rupture or damage of the horizontal internal or external patellar ligaments;injury can develop with frequent, long-term microtrauma of the ligaments, for example, during jumping;it is accompanied by bleeding into the joint cavity (hemarthrosis);the pain is strong, constant, accompanied by swelling;leg movement is impaired.
In order to avoid permanent dysfunction of the joint at the site of the injury, immediately seek help from an orthopedic traumatologist.
Knee pain radiating to the leg, heel, and groin
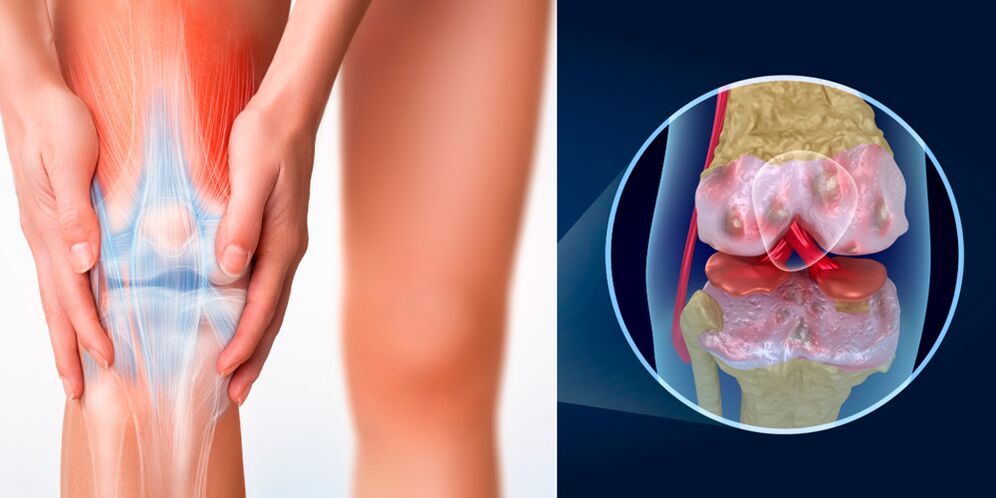
The causes of acute radiating pain in the knee must be understood.This may be due to:
- femoral nerve entrapment;the pain is acute, piercing, starts sharply in the groin area, spreads along the front-inner surface of the thigh and knee, can reach the inner edge of the foot and heel along the nerve branches;sometimes the patient has the impression that his knee hurts, but this is not so;
- arthritis of various origins (gonarthritis): joint swelling leads to pinching of nerves and the spread of sharp pain in the knee to the groin and heel;in this case, aching pain is mainly felt in the knee, which turns into acute pain with irradiation above and below the knee with sudden movements;
- bruising accompanied by hemarthrosis, ligament rupture, severe swelling and compression of nerves;
- contusion by breaking or dislocating the patella and causing the joint to become out of balance;acute pain in the knee extends down the thigh to the groin, along the inner surface of the tibia - lower, to the heel.
This type of severe knee pain requires immediate medical attention.Folk remedies do not help, an ambulance must be called.
Knee pain when stretching and bending
Most often, pain in the knee during bending and stretching, as well as squatting, is a sign of tendinitis - an inflammatory process in the area of the tendon-ligament apparatus of the knee joint.It develops mainly in young sportsmen and is the result of frequent repetitive microtraumas associated with jumping and constant shaking of the limb.The first sign is an inability to straighten the knee without pain.
The cause of painful knee bending and extension can also be arthrosis - degenerative-dystrophic changes in the joint with the growth of connective and bone tissue, which interferes with movement.
Only the treatment of tendinitis or arthrosis helps relieve the patient from severe knee pain when bending and extending.
Severe knee pain at night
Pain at night is characteristic of inflammatory processes.This can be latent arthritis, periodically inflamed knee joint due to arthrosis (arthrosis-arthritis).During sleep, joints and periarticular tissues heat up, blood vessels dilate, which increases swelling.
The periarticular tissues swell, compressing the nerve endings and causing pain.If, at the same time, there is pain behind the knee, this may be a sign of a Baker's cyst.How to get rid of swelling and pain at night?Treating the underlying disease helps.
Knee pain when walking
Movement, jogging, nagging pain under the knee are typical of degenerative-dystrophic processes of the knee - arthrosis, because during movement the joint surfaces are damaged, completely or partially free of shock-absorbing cartilage.The well-innervated periosteum suffers.Knee pain when descending stairs is also very common.After training, patients note that the pain in the knee continues to hurt for some time.Over time, pain appears in the foot.
Long-term rehabilitation treatment helps with the use of chondroprotectors - drugs for the restoration of cartilage tissue.In case of complete destruction of the joint - endoprosthesis.
Pain after exercise - squatting, running, lifting weights
This indicates long-term microtrauma of the knee joints and the gradual development of degenerative-dystrophic processes in them.Sometimes pain occurs in one of the right or left knees.The joints are crumbling.
If severe pain occurs in the knee after training, the athlete needs rehabilitation treatment.Otherwise, there will be a gradual decrease in joint functions, accompanied by first intermittent and then constant pain.
Knee pain and crunch
Sharp, sudden knee pain and cracking (crunching) indicate a tear in the meniscus, the cartilaginous shock-absorbing pads in the knee joint.This may be due to injury or age-related wear and tear of cartilage structures.
Severe joint pains may go away, but knee pain persists when squatting, then limb dysfunction gradually increases, first accompanied by pain during exercise, then constant pain, which intensifies when walking down the stairs.Over time, the entire limb suffers and crunches, including the foot.Long-term rehabilitation treatment under the supervision of an orthopedic traumatologist helps.
Knee pain and swelling
Pain accompanied by swelling always indicates the presence of an inflammatory process.It can be aseptic (without infection, usually after an injury), infectious, infectious-allergic and autoimmune (allergic to one's own tissues).
To get rid of such pain, you need to determine the cause and carry out the treatment prescribed by the specialist.
Injuries and diseases that cause knee pain
The most common pathologies accompanying knee pain are:
- Closed and open knee injuries with intra-articular fractures, dislocations, meniscal tears.All of them lead to the development of inflammatory processes (arthritis), which turn into degenerative-dystrophic processes (arthrosis), with the development of constant pain and knee dysfunction.This is the most common cause of knee pain.Athletes are at risk.Even a minor knee injury can cause the destruction of joint tissue cells, which leads to the development of an inflammatory process.In case of significant injuries, all these processes are pronounced and involve long-lasting pain.The instability of the knee, which develops when the ligament apparatus is damaged, is of great importance.Over time, instability increases, nearby tissues are damaged, which causes increased pain in the knee joint, especially when going down stairs.In the absence of proper treatment, the process can be complicated by infection, become purulent, endanger the patient's life, or become chronic with gradual progression and destruction of the joint, accompanied by severe pain.
- Arthritis of the knee joint is an inflammatory process of various origins, which is accompanied by an increase in body temperature and disruption of the patient's general condition.Patients complain that the pain in the knee hurts constantly.The disease can be infectious, infectious-allergic, autoimmune, or metabolic in nature.The inflammatory process takes place differently depending on the underlying cause (purulent, rheumatic, psoriatic, gouty and other arthritis).Sometimes arthritis can be complicated by a Baker's cyst in the popliteal region.Then pain appears behind the knee.Only proper treatment prescribed by a traumatologist or rheumatologist can save you from joint destruction and disability.
- Knee arthrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic process in the joint that develops after injuries, acute and chronic inflammatory processes, and against the background of age-related metabolic disorders in the elderly.The shock-absorbing tissue of the cartilage (menisci and the cartilaginous layer covering the joint surface of the bones) is destroyed or thinned.The destruction of the joint progresses slowly but steadily.I am concerned about the pain and cracking when moving.In old age, this is the main cause of knee pain.The bones rub against each other, their structure is destroyed, the joint is deformed, all accompanied by severe pain.
- Cysts and tumors.
How to treat severe knee pain
Injuries and diseases of the knee often lead to patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS), which is pain in the front of the knee joint.Changes in the joint gradually destroy the patellar cartilage, contributing to joint instability and constant severe knee pain.Only rehabilitation treatment prescribed by a qualified specialist can help.
Diagnostics
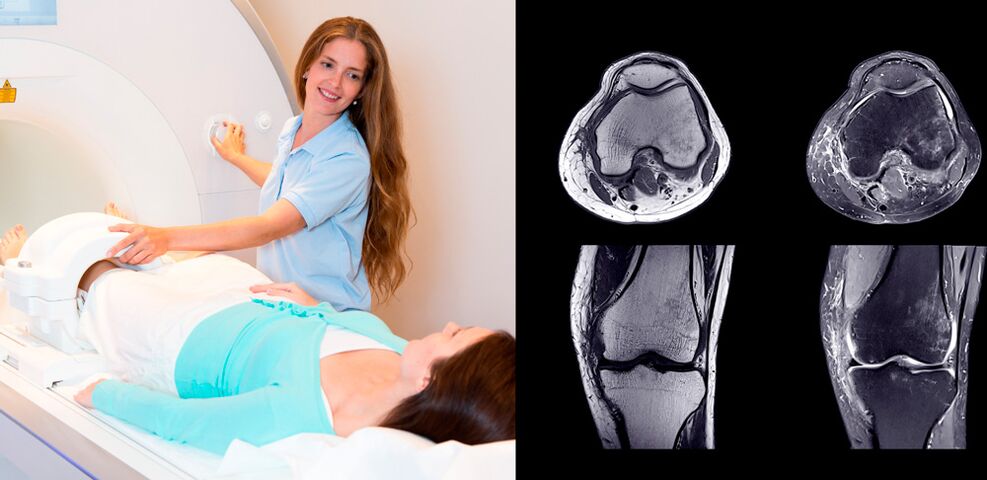
Knee pain has different causes and treatment requires an individual approach.First of all, a correct diagnosis must be made, and this requires a clinical examination.And only after that, the treatment of knee pain is prescribed.
Some diseases cannot be completely cured, but a doctor can eliminate the pain and stop the destruction of the joint.
To determine the causes of pain and to diagnose the disease, the following examination should be performed:
- Laboratory tests- clinical, biochemical, immunological blood test, if necessary - sampling and examination of intra-articular fluid (microscopy, culture on medium to determine the antibiotic sensitivity of the identified infection).
- Instrumental studies: Ultrasound– reveals soft tissue pathology and the amount of intra-articular fluid radiography– changes in the bone tissue of the knee; CT and MRI– a more detailed study of soft and hard tissue pathology; diagnostic arthroscopy- appearance and changes in the joint membrane of the knee.
Methods for treating severe knee pain
Treatment measures are prescribed individually.Pain associated with a knee injury is treated by an orthopedic traumatologist;if the disease becomes chronic, a rheumatologist consultation is necessary.If there is a suspicion of a purulent inflammatory process, then the surgeon is better able to treat the disease.All chronic inflammatory processes of the joints are treated by a rheumatologist, but certain infectious processes, such as tuberculosis of the knee, are treated by a phthisisist or other specialist closely related to a rheumatologist.
Above all, they try to eliminate the pain as much as possible, using both drug therapy (modern drugs for knee pain, including ointments) and non-drug remedies for knee pain (manual therapy, massage, physiotherapy, reflexology courses and other traditional methods, folk remedies).In order to reduce the load on the joint and create rest, various immobilization methods are used (splints, splints), as well as taping - fixing the joint with special adhesive tapes.
In all cases of acute joint pain, we perform an emergency examination of the patient with simultaneous anesthesia.During the treatment, all modern and traditional methods of pain therapy are used.After that, the patient is either hospitalized or prescribed outpatient treatment, followed by rehabilitation.No patient in pain is left without the attention of a specialist.



















